用 JavaScript 實作堆疊(Stack)
2021-11-21 · 5 min read
如先前文章所言,本系列文章會以 JavaScript 學習演算法與資料結構為主題來撰寫。
本系列主要參考自以下資料:
- 石田保輝 和 宮崎修一 的 演算法圖鑑
- Colt Steele 的 JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures Masterclass
此外,如果想以圖像的方式了解資料結構及演算法,也很推薦參考 VisuAlgo。
預備知識
了解本文內容之前需要具備的 prerequisite:
- JavaScript 基礎知識及 ES6 語法
- 物件導向觀念
- Big O Notation
- 資料結構的基礎理解
- 資料結構 Singly Linked List
以上內容不會在本文說明,如果想了解可以參考以下外部連結
- JavaScript Class 語法,可參考 [教學] 深入淺出 JavaScript ES6 Class (類別) | Shubo 的程式教學筆記
- Big O Notation,可參考【演算法】時間複雜度與空間複雜度 Time & Space Complexity - Jason Chen's Blog
另外我有寫過 Singly Linked List 的文章,可以參考
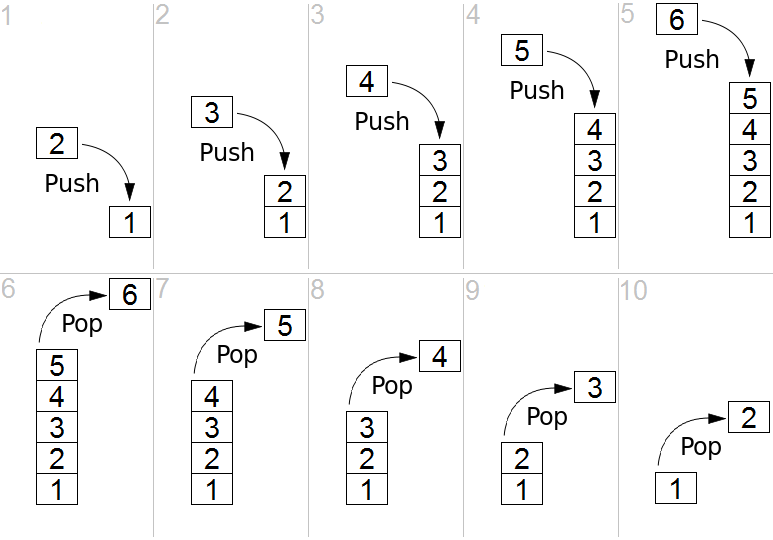
什麼是 Stack?
資料像紙本文件由下往上堆疊一樣,只能從最新追加的資料開始存取。
後追加的數據先取出的特性是 「後進先出」,即「Last In First Out」縮寫「LIFO」。
 source: Stack (abstract data type) - Wikipedia
source: Stack (abstract data type) - Wikipedia
解說
應用
Stack 的特性就是取得最新的資料,所以有這種需求的應用會適合用 stack 來處理,例如:
- 瀏覽器的 call stack
- Undo / Redo 功能
- 歷史紀錄
實作
JavaScript 本來就具有 Array 這個 data type,其實就可以直接拿來實現 stack,像是利用 array 的 push 放入 data 到最後一個 index,要取出時用 pop 就可取出最新的 data。
let stack = [];
stack.push(0);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.pop();
由於 push 和 pop 兩個 method 都是變動 array 最後面的元素,不會改變 array 裡其他元素的順序,因此 Big O 是 O(1)。
Object Property
這部分用物件導向的方式來實作,一個 stack 由數個 node 組成,他們各自是一種 object。
node 具有:
- value
- pointer to next node(指向下一個 node 或 null)
Stack 具有:
- first node
- last node
- size
因此可以用 OOP 物件導向的方式來定義他們:
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
}
Object Method
Doubly Linked List 具有以下 method:
Pushing
push 即增加一個 node 到 stack 的最前面的位置
Pseudocode:
- function 要接收一個 value
- 利用 function 接收的 value 來建立一個新的 node
- 如果 stack 沒有 node,則把 first 與 last 都設為剛建立的新 node
-
如果 stack 裡有 node 的話
- 新 node 的 next 設為 first
- 把 first 設為新 node
- 將 stack 的 size 增加 1
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
push(val) {
var newNode = new Node(val);
if (this.size === 0) {
this.first = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = this.first;
this.first = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
}
Popping
pop 是將 stack 最後一個加入的 node 拿出來
Pseudocode:
- 如果 stack 沒有 node,則 return null
-
如果 stack 有 node
- 把 first 放入一個新變數 target node
- 如果 first 和 last 是同一個 node,則設 last 為 null
- 將 target node 的 next 設為新的 first
- stack 的 size 減 1
- return target node 的 value
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
...
pop() {
if (this.size === 0) return null;
const targetNode = this.first;
if (this.first === this.last) {
this.last === null;
}
this.first = targetNode.next;
this.size--;
return targetNode.val;
}
}
總結
最終關於 Stack 的定義會是這樣:
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
push(val) {
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (this.size === 0) {
this.first = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = this.first;
this.first = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
pop() {
if (this.size === 0) return null;
const targetNode = this.first;
if (this.first === this.last) {
this.last === null;
}
this.first = targetNode.next;
this.size--;
return targetNode.val;
}
}
Stack 的 Big O
- Insertion - O(1)
- Removal - O(1)
- Searching - O(N)
- Access - O(N)
Stack 的追加和刪除資料都是從 first 開始處理,只要處理兩個 node 之間的關聯即可,效率很高是 O(1)。
但存取資料就不是 stack 的強項,如果要搜尋某個 node,就需要像 Singly Linked List 從頭開始一個接一個的 next 下去,所以若有這種功能的需求,應該優先考慮其他種資料結構。